Vuex
Last updated
Nov 1, 2021
##1.Vuex概述
Vuex是实现组件全局状态(数据)管理的一种机制,可以方便的实现组件之间的数据共享
使用Vuex管理数据的好处:
A.能够在vuex中集中管理共享的数据,便于开发和后期进行维护
B.能够高效的实现组件之间的数据共享,提高开发效率
C.存储在vuex中的数据是响应式的,当数据发生改变时,页面中的数据也会同步更新
使用 Vue 我们就不可避免的会遇到组件间共享的数据或状态。应用的业务代码逐渐复杂,props、事件、事件总线等通信的方式的弊端就会愈发明显。这个时候我们就需要 Vuex 。Vuex 是一个专门为 Vue 设计的状态管理工具。
状态管理是 Vue 组件解耦的重要手段。

# 2.Vuex的基本使用
Vuex 不限制你的代码结构,但需要遵守一些规则:
- 应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中
- 提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的
- 异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面
创建带有vuex的vue项目,打开终端,输入命令:vue ui
当项目仪表盘打开之后,我们点击页面左上角的项目管理下拉列表,再点击Vue项目管理器
点击创建项目,如下图所示
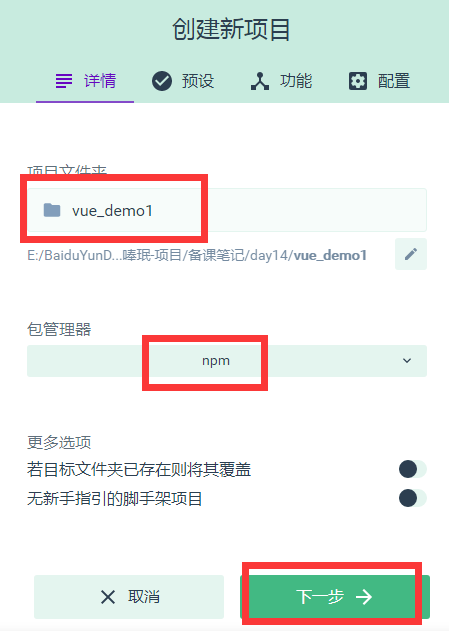
第一步,设置项目名称和包管理器
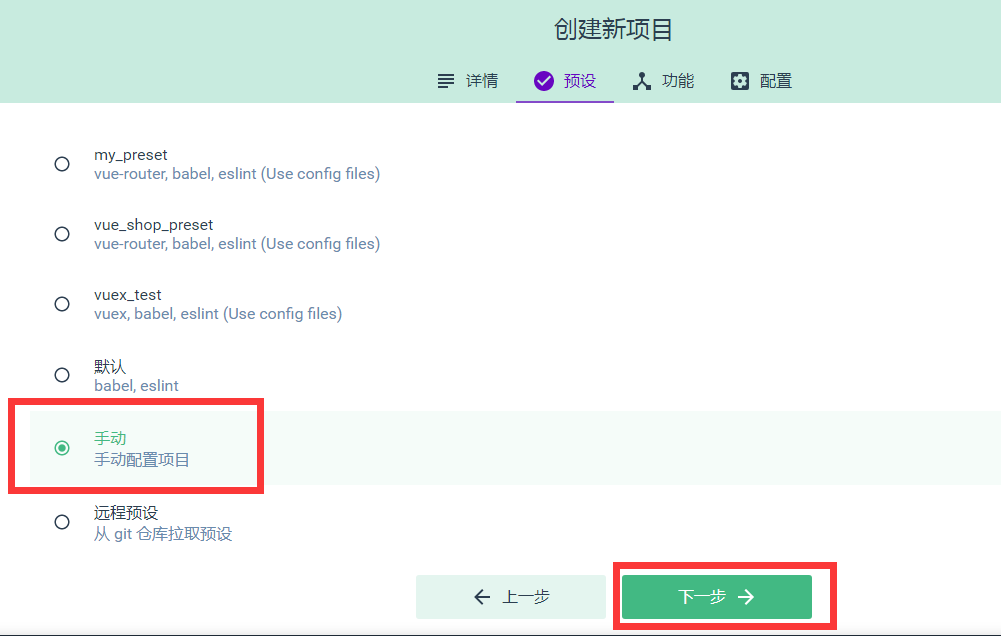
第二步,设置手动配置项目
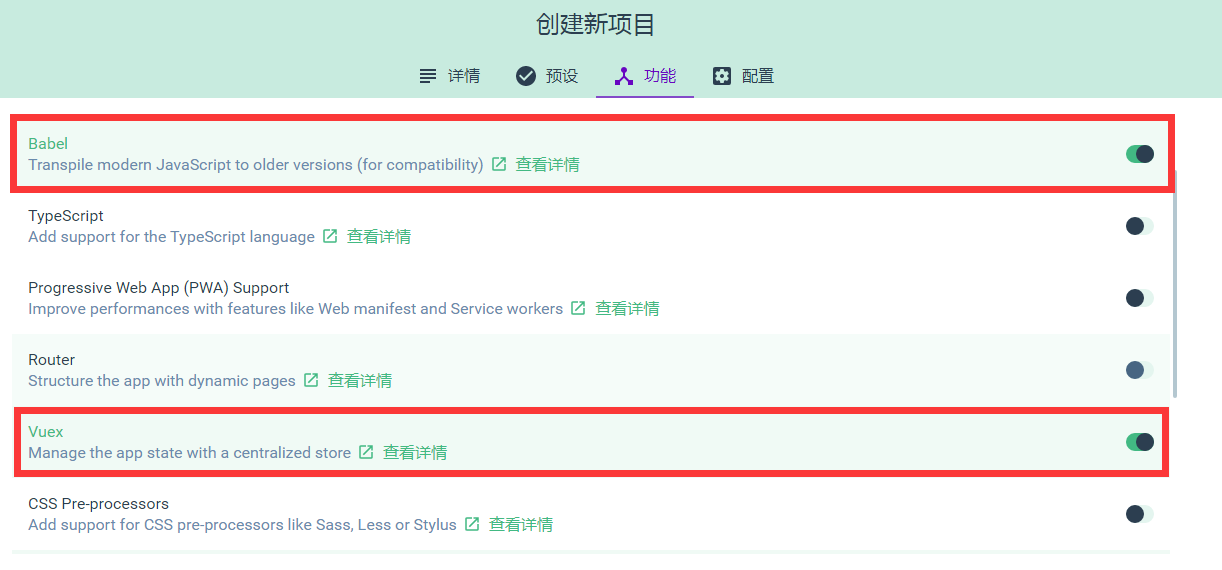
第三步,设置功能项
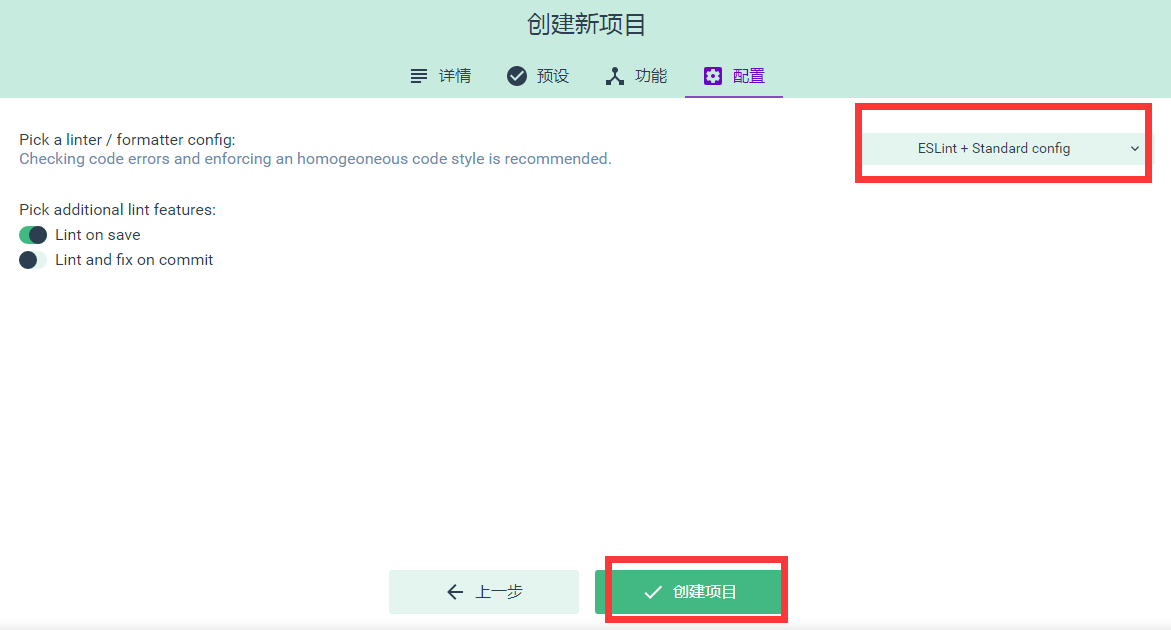
.png)
第四步,创建项目
##3.使用Vuex完成计数器案例
打开刚刚创建的vuex项目,找到src目录中的App.vue组件,将代码重新编写如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <template>
<div>
<my-addition></my-addition>
<p>----------------------------------------</p>
<my-subtraction></my-subtraction>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Addition from './components/Addition.vue'
import Subtraction from './components/Subtraction.vue'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
components: {
'my-subtraction': Subtraction,
'my-addition': Addition
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|
在components文件夹中创建Addition.vue组件,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:</h3>
<button>+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|
在components文件夹中创建Subtraction.vue组件,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <template>
<div>
<h3>当前最新的count值为:</h3>
<button>-1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
|
最后在项目根目录(与src平级)中创建 .prettierrc 文件,编写代码如下:
1
2
3
4
| {
"semi":false,
"singleQuote":true
}
|
##4.Vuex中的核心特性
####A.State
State提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store中的State中存储
例如,打开项目中的store.js文件,在State对象中可以添加我们要共享的数据,如:count:0
在组件中访问State的方式:
this.\$store.state.全局数据名称 如:this.$store.state.count
先按需导入mapState函数: import { mapState } from 'vuex'
然后数据映射为计算属性: computed:{ …mapState(['全局数据名称']) }
####B.Mutation
Mutation用于修改变更$store中的数据
使用方式:
打开store.js文件,在mutations中添加代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| mutations: {
add(state,step){
//第一个形参永远都是state也就是$state对象
//第二个形参是调用add时传递的参数
state.count+=step;
}
}
|
然后在Addition.vue中给按钮添加事件代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <button @click="Add">+1</button>
methods:{
Add(){
//使用commit函数调用mutations中的对应函数,
//第一个参数就是我们要调用的mutations中的函数名
//第二个参数就是传递给add函数的参数
this.$store.commit('add',10)
}
}
|
使用mutations的第二种方式:
1
2
3
4
5
| import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapMutations(['add'])
}
|
如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import { mapState,mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
methods:{
//获得mapMutations映射的sub函数
...mapMutations(['sub']),
//当点击按钮时触发Sub函数
Sub(){
//调用sub函数完成对数据的操作
this.sub(10);
}
},
computed:{
...mapState(['count'])
}
}
|
####C.Action
在mutations中不能编写异步的代码,会导致vue调试器的显示出错。
在vuex中我们可以使用Action来执行异步操作。
操作步骤如下:
打开store.js文件,修改Action,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| actions: {
addAsync(context,step){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add',step);
},2000)
}
}
|
然后在Addition.vue中给按钮添加事件代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <button @click="AddAsync">...+1</button>
methods:{
AddAsync(){
this.$store.dispatch('addAsync',5)
}
}
|
第二种方式:
1
2
3
4
5
| import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapActions(['subAsync'])
}
|
如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import { mapState,mapMutations,mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {}
},
methods:{
//获得mapMutations映射的sub函数
...mapMutations(['sub']),
//当点击按钮时触发Sub函数
Sub(){
//调用sub函数完成对数据的操作
this.sub(10);
},
//获得mapActions映射的addAsync函数
...mapActions(['subAsync']),
asyncSub(){
this.subAsync(5);
}
},
computed:{
...mapState(['count'])
}
}
|
####D.Getter
Getter用于对Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据
它只会包装Store中保存的数据,并不会修改Store中保存的数据,当Store中的数据发生变化时,Getter生成的内容也会随之变化
打开store.js文件,添加getters,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| export default new Vuex.Store({
.......
getters:{
//添加了一个showNum的属性
showNum : state =>{
return '最新的count值为:'+state.count;
}
}
})
|
然后打开Addition.vue中
添加插值表达式使用getters,{{$store.getters.showNum}}
也可以在Addition.vue中,导入mapGetters,并将之映射为计算属性
1
2
3
4
| import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed:{
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
}
|
##5.vuex案例
####A.初始化案例
首先使用vue ui初始化一个使用vuex的案例
然后打开public文件夹,创建一个list.json文件,文件代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| [
{
"id": 0,
"info": "Racing car sprays burning fuel into crowd.",
"done": false
},
{
"id": 1,
"info": "Japanese princess to wed commoner.",
"done": false
},
{
"id": 2,
"info": "Australian walks 100km after outback crash.",
"done": false
},
{
"id": 3,
"info": "Man charged over missing wedding girl.",
"done": false
},
{
"id": 4,
"info": "Los Angeles battles huge wildfires.",
"done": false
}
]
|
再接着,打开main.js,添加store.js的引入,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store.js'
// 1. 导入 ant-design-vue 组件库
import Antd from 'ant-design-vue'
// 2. 导入组件库的样式表
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/antd.css'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 3. 安装组件库
Vue.use(Antd)
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
|
再接着打开store.js,添加axios请求json文件获取数据的代码,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import axios from 'axios'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//所有任务列表
list: [],
//文本输入框中的值
inputValue: 'AAA'
},
mutations: {
initList(state, list) {
state.list = list
},
setInputValue(state,value){
state.inputValue = value
}
},
actions: {
getList(context) {
axios.get('/list.json').then(({ data }) => {
console.log(data);
context.commit('initList', data)
})
}
}
})
|
最后,代开App.vue文件,将store中的数据获取并展示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| <template>
<div id="app">
<a-input placeholder="请输入任务" class="my_ipt" :value="inputValue" @change="handleInputChange" />
<a-button type="primary">添加事项</a-button>
<a-list bordered :dataSource="list" class="dt_list">
<a-list-item slot="renderItem" slot-scope="item">
<!-- 复选框 -->
<a-checkbox :checked="item.done">{{item.info}}</a-checkbox>
<!-- 删除链接 -->
<a slot="actions">删除</a>
</a-list-item>
<!-- footer区域 -->
<div slot="footer" class="footer">
<!-- 未完成的任务个数 -->
<span>0条剩余</span>
<!-- 操作按钮 -->
<a-button-group>
<a-button type="primary">全部</a-button>
<a-button>未完成</a-button>
<a-button>已完成</a-button>
</a-button-group>
<!-- 把已经完成的任务清空 -->
<a>清除已完成</a>
</div>
</a-list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'app',
data() {
return {
// list:[]
}
},
created(){
// console.log(this.$store);
this.$store.dispatch('getList')
},
methods:{
handleInputChange(e){
// console.log(e.target.value)
this.$store.commit('setInputValue',e.target.value)
}
},
computed:{
...mapState(['list','inputValue'])
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#app {
padding: 10px;
}
.my_ipt {
width: 500px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.dt_list {
width: 500px;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.footer {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
</style>
|
####B.完成添加事项
首先,打开App.vue文件,给“添加事项”按钮绑定点击事件,编写处理函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| //绑定事件
<a-button type="primary" @click="addItemToList">添加事项</a-button>
//编写事件处理函数
methods:{
......
addItemToList(){
//向列表中新增事项
if(this.inputValue.trim().length <= 0){
return this.$message.warning('文本框内容不能为空')
}
this.$store.commit('addItem')
}
}
|
然后打开store.js编写addItem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
//所有任务列表
list: [],
//文本输入框中的值
inputValue: 'AAA',
//下一个id
nextId:5
},
mutations: {
........
//添加列表项
addItem(state){
const obj = {
id :state.nextId,
info: state.inputValue.trim(),
done:false
}
//将创建好的事项添加到数组list中
state.list.push(obj)
//将nextId值自增
state.nextId++
state.inputValue = ''
}
}
......
})
|
####C.完成删除事项
首先,打开App.vue文件,给“删除”按钮绑定点击事件,编写处理函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| //绑定事件
<a slot="actions" @click="removeItemById(item.id)">删除</a>
//编写事件处理函数
methods:{
......
removeItemById(id){
//根据id删除事项
this.$store.commit('removeItem',id)
}
}
|
然后打开store.js编写addItem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| export default new Vuex.Store({
......
mutations: {
........
removeItem(state,id){
//根据id删除事项数据
const index = state.list.findIndex( x => x.id === id )
// console.log(index);
if(index != -1) state.list.splice(index,1);
}
}
......
})
|
####D.完成选中状态的改变
首先,打开App.vue文件,给“复选”按钮绑定点击事件,编写处理函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| //绑定事件
<a-checkbox :checked="item.done" @change="cbStateChanged(item.id,$event)">{{item.info}}</a-checkbox>
//编写事件处理函数
methods:{
......
cbStateChanged(id,e){
//复选框状态改变时触发
const param = {
id:id,
status:e.target.checked
}
//根据id更改事项状态
this.$store.commit('changeStatus',param)
}
}
|
然后打开store.js编写addItem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| export default new Vuex.Store({
......
mutations: {
........
changeStatus(state,param){
//根据id改变对应事项的状态
const index = state.list.findIndex( x => x.id === param.id )
if(index != -1) state.list[index].done = param.status
}
}
......
})
|
####E.剩余项统计
打开store.js,添加getters完成剩余项统计
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| getters:{
unDoneLength(state){
const temp = state.list.filter( x => x.done === false )
console.log(temp)
return temp.length
}
}
|
打开App.vue,使用getters展示剩余项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| //使用映射好的计算属性展示剩余项
<!-- 未完成的任务个数 -->
<span>{{unDoneLength}}条剩余</span>
//导入getters
import { mapState,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
//映射
computed:{
...mapState(['list','inputValue']),
...mapGetters(['unDoneLength'])
}
|
####F.清除完成事项
首先,打开App.vue文件,给“清除已完成”按钮绑定点击事件,编写处理函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <!-- 把已经完成的任务清空 -->
<a @click="clean">清除已完成</a>
//编写事件处理函数
methods:{
......
clean(){
//清除已经完成的事项
this.$store.commit('cleanDone')
}
}
|
然后打开store.js编写addItem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| export default new Vuex.Store({
......
mutations: {
........
cleanDone(state){
state.list = state.list.filter( x => x.done === false )
}
}
......
})
|
####G.点击选项卡切换事项
打开App.vue,给“全部”,“未完成”,“已完成”三个选项卡绑定点击事件,编写处理函数
并将列表数据来源更改为一个getters。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <a-list bordered :dataSource="infoList" class="dt_list">
......
<!-- 操作按钮 -->
<a-button-group>
<a-button :type="viewKey ==='all'?'primary':'default'" @click="changeList('all')">全部</a-button>
<a-button :type="viewKey ==='undone'?'primary':'default'" @click="changeList('undone')">未完成</a-button>
<a-button :type="viewKey ==='done'?'primary':'default'" @click="changeList('done')">已完成</a-button>
</a-button-group>
......
</a-list>
//编写事件处理函数以及映射计算属性
methods:{
......
changeList( key ){
//点击“全部”,“已完成”,“未完成”时触发
this.$store.commit('changeKey',key)
}
},
computed:{
...mapState(['list','inputValue','viewKey']),
...mapGetters(['unDoneLength','infoList'])
}
|
打开store.js,添加getters,mutations,state
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
......
//保存默认的选项卡值
viewKey:'all'
},
mutations: {
......
changeKey(state,key){
//当用户点击“全部”,“已完成”,“未完成”选项卡时触发
state.viewKey = key
}
},
......
getters:{
.......
infoList(state){
if(state.viewKey === 'all'){
return state.list
}
if(state.viewKey === 'undone'){
return state.list.filter( x => x.done === false )
}
if(state.viewKey === 'done'){
return state.list.filter( x => x.done === true )
}
}
}
})
|
# Vuex 注入 Vue 生命周期的过程
我们在安装插件的时候,总会像下面一样用 Vue.use() 来载入插件,可是 Vue.use() 做了什么呢?
1
2
3
4
| import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
|
# Vue.use() 做了什么
安装 Vue.js 插件。如果插件是一个对象,必须提供 install 方法。如果插件是一个函数,它会被作为 install 方法。install 方法调用时,会将 Vue 作为参数传入。
以上是 官方文档 的解释。
接下来我们从源码部分来看看 Vue.use() 都做了什么。
Vue 源码在 initGlobalAPI 入口方法中调用了 initUse (Vue) 方法,这个方法定义了 Vue.use() 需要做的内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| function initGlobalAPI (Vue) {
......
initUse(Vue);
initMixin$1(Vue); // 下面讲 Vue.mixin 会提到
......
}
function initUse (Vue) {
Vue.use = function (plugin) {
var installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []));
/* 判断过这个插件是否已经安装 */
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
var args = toArray(arguments, 1);
args.unshift(this);
/* 判断插件是否有 install 方法 */
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args);
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args);
}
installedPlugins.push(plugin);
return this
};
}
|
这段代码主要做了两件事情:
- 一件是防止重复安装相同的 plugin
- 另一件是初始化 plugin
# 插件的 install 方法
看完以上源码,我们知道插件(Vuex)需要提供一个 install 方法。那么我们看看 Vuex 源码中是否有这个方法。结果当然是有的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| /* 暴露给外部的 install 方法 */
function install (_Vue) {
/* 避免重复安装(Vue.use 内部也会检测一次是否重复安装同一个插件)*/
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
{
console.error(
'[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
);
}
return
}
Vue = _Vue;
/* 将 vuexInit 混淆进 Vue 的 beforeCreate(Vue2.0) 或 _init 方法(Vue1.0) */
applyMixin(Vue);
}
|
这段代码主要做了两件事情:
- 一件是防止 Vuex 被重复安装
- 另一件是执行
applyMixin,目的是执行 vuexInit 方法初始化 Vuex
接下来 我们看看 applyMixin(Vue) 源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| /* 将 vuexInit 混淆进 Vue 的 beforeCreate */
function applyMixin (Vue) {
var version = Number(Vue.version.split('.')[0]);
if (version >= 2) {
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit });
} else {
/* Vue1.0 的处理逻辑,此处省略 */
......
}
function vuexInit () {
......
}
}
|
从上面的源码,可以看出 Vue.mixin 方法将 vuexInit 方法混淆进 beforeCreate 钩子中,也是因为这个操作,所以每一个 vm 实例都会调用 vuexInit 方法。那么 vuexInit 又做了什么呢?
# vuexInit()
我们在使用 Vuex 的时候,需要将 store 传入到 Vue 实例中去。
1
2
3
4
| new Vue({
el: '#app',
store
});
|
但是我们却在每一个 vm 中都可以访问该 store,这个就需要靠 vuexInit 了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function vuexInit () {
const options = this.$options
if (options.store) {
/* 根节点存在 stroe 时 */
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
/* 子组件直接从父组件中获取 $store,这样就保证了所有组件都公用了全局的同一份 store*/
this.$store = options.parent.$store
}
}
|
根节点存在 stroe 时,则直接将 options.store 赋值给 this.$store。否则则说明不是根节点,从父节点的 $store 中获取。
通过这步的操作,我们就以在任意一个 vm 中通过 this.$store 来访问 Store 的实例。接下来我们反过来说说 Vue.mixin()。
# Vue.mixin()
全局注册一个混入,影响注册之后所有创建的每个 Vue 实例。插件作者可以使用混入,向组件注入自定义的行为。不推荐在应用代码中使用。
在 vue 的 initGlobalAPI 入口方法中调用了 initMixin$1(Vue) 方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| function initMixin$1 (Vue) {
Vue.mixin = function (mixin) {
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin);
return this
};
}
|
Vuex 注入 Vue 生命周期的过程大概就是这样,如果你感兴趣的话,你可以直接看看 Vuex 的源码,接下来我们说说 Store。
# Store
上面我们讲到了 vuexInit 会从 options 中获取 Store。所以接下来会讲到 Store 是怎么来的呢?
我们使用 Vuex 的时候都会定义一个和下面类似的 Store 实例。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import mutations from './mutations'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const state = {
showState: 0,
}
export default new Vuex.Store({
strict: true,
state,
getters,
})
|
不要在发布环境下启用严格模式。严格模式会深度监测状态树来检测不合规的状态变更 —— 请确保在发布环境下关闭严格模式,以避免性能损失。
# state 的响应式
你是否关心 state 是如何能够响应式呢?这个主要是通过 Store 的构造函数中调用的 resetStoreVM(this, state) 方法来实现的。
这个方法主要是重置一个私有的 _vm(一个 Vue 的实例) 对象。这个 _vm 对象会保留我们的 state 树,以及用计算属性的方式存储了 store 的 getters。现在具体看看它的实现过程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| /* 使用 Vue 内部的响应式注册 state */
function resetStoreVM (store, state, hot) {
/* 存放之前的vm对象 */
const oldVm = store._vm
store.getters = {}
const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
const computed = {}
/* 通过 Object.defineProperty 方法为 store.getters 定义了 get 方法。当在组件中调用 this.$store.getters.xxx 这个方法的时候,会访问 store._vm[xxx]*/
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
computed[key] = partial(fn, store)
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
const silent = Vue.config.silent
/* 设置 silent 为 true 的目的是为了取消 _vm 的所有日志和警告 */
Vue.config.silent = true
/* 这里new了一个Vue对象,运用Vue内部的响应式实现注册state以及computed*/
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
})
Vue.config.silent = silent
/* 使能严格模式,Vuex 中对 state 的修改只能在 mutation 的回调函数里 */
if (store.strict) {
enableStrictMode(store)
}
if (oldVm) {
/* 解除旧 vm 的 state 的引用,并销毁这个旧的 _vm 对象 */
if (hot) {
store._withCommit(() => {
oldVm._data.$$state = null
})
}
Vue.nextTick(() => oldVm.$destroy())
}
}
|
state 的响应式大概就是这样实现的,也就是初始化 resetStoreVM 方法的过程。
# 看看 Store 的 commit 方法
我们知道 commit 方法是用来触发 mutation 的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| commit (_type, _payload, _options) {
/* unifyObjectStyle 方法校参 */
const {
type,
payload,
options
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
const mutation = { type, payload }
/* 找到相应的 mutation 方法 */
const entry = this._mutations[type]
if (!entry) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown mutation type: ${type}`)
}
return
}
/* 执行 mutation 中的方法 */
this._withCommit(() => {
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
/* 通知所有订阅者,传入当前的 mutation 对象和当前的 state */
this._subscribers.forEach(sub => sub(mutation, this.state))
if (
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
options && options.silent
) {
console.warn(
`[vuex] mutation type: ${type}. Silent option has been removed. ` +
'Use the filter functionality in the vue-devtools'
)
}
}
|
该方法先进行参数风格校验,然后利用 _withCommit 方法执行本次批量触发 mutation 处理函数。执行完成后,通知所有 _subscribers(订阅函数)本次操作的 mutation 对象以及当前的 state状态。




